22.09.2021
10 Things to know about… Real Time Locating Systems (RTLS)
1) Definition
The ISO/IEC FDIS 19762-5 standard defines RTLS as follows: It is a combination of hardware and software used to continuously determine and provide the real-time location of assets that are equipped with devices that can communicate with the system.
2) Limitations
Technically, locating a cell phone via GPS is also a real-time location system – but not formally, according to ISO/IEC FDIS 19762-5. According to the standard, real-time location systems are always tied to a fixed facility and to the willing carrying of an RTLS identifier.
3) The Compliance Question
For GDPR compliance, real-time positioning of individuals always requires the explicit consent of the individual being localized to comply with the right to informational self-determination.
4) Indoor RTLS
Since real-time indoor location cannot be implemented via GPS due to architectural limitations, other technologies based on the transmitter-receiver principle are used here. Among the best known and most effective are Bluetooth Low Energy, WLAN and UWB. In contrast to position determination via GPS, these technologies can also be used to determine the position of an object on different floors of a building.
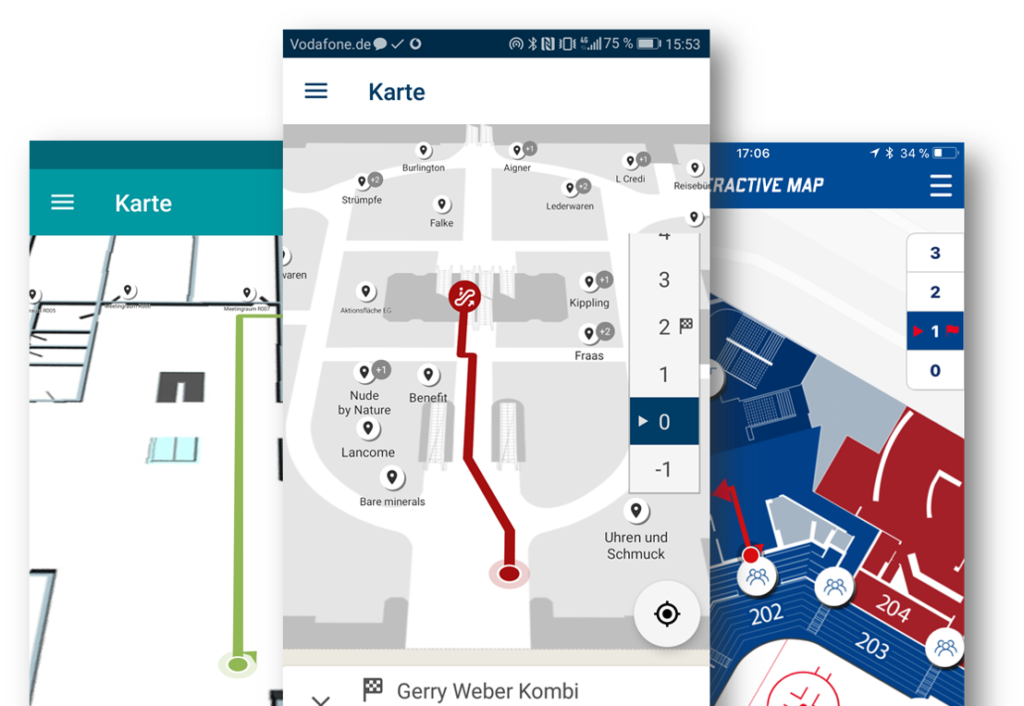
5) The “Blue dot”
The “blue dot” produced by real-time location systems based on a transmitter-receiver infrastructure can be used for various real-time location services: Indoor Navigation, Asset Tracking and Proximity Notifications. Additional added value can be generated by the fact that the collected data can be integrated, for example, into a company’s own ERP system, SAP or an IoT platform and used for process optimization.
6) 3 Levels of accuracy
Bluetooth Low Energy enables three levels of accuracy depending on the use case: Presence: is my object inside a building or not? Proximity: in which zone of the building is my object located? Positioning: at which position – accurate to 1-3 meters – is my object located? With the Angle-of-Arrival method, an even higher accuracy of up to 10 cm is possible.
7) The Locating Engine
The heart of a Real Time Location System is the Locating Engine – also called Positioning Engine. The Locating Engine combines geometric or topographic algorithms with filter algorithms to calculate the position of an object as accurately as possible and in real time.
8) Versatility
RTLS are relevant for a wide variety of verticals. Always under the premise that data protection requirements are met, they can be used in office complexes, public buildings, hospitals, shopping malls, industrial and manufacturing facilities, logistics, at transportation hubs, in mining and surface mining, or even on cruise ships.
9) Resilience
Bluetooth-based RTLS also work in hazardous, explosive, electromagnetic or architecturally challenging environments. Hardware with the appropriate IP rating and certification (e.g., ATEX) is then required.
10) Real time tracking indoors & outdoors
Meanwhile, a combination of different technologies also makes a seamless transition between indoor and outdoor possible. As an example, a combination of Bluetooth Low Energy indoors and GPS/LoRaWAN outdoors is possible. Favendo offers this combined indoor/outdoor tracking solution together with its partner Actility and their subsidiary Abeeway. Arrange a free consultation here